No, a transmission and a gearbox are not the same. The gearbox is one part of the transmission system. You should know this difference. If you mix up these words, you could make expensive mistakes. You might forget to check transmission fluid or use the clutch right. Missing these steps can make your car overheat. It can also wear out parts too soon and cost a lot to fix.
You should check transmission fluid every 20,000 miles.
Using the clutch the right way keeps your gearbox working well.
Taking care of your car often helps you stop big problems with your transmission gearbox.
The transmission moves power from the engine to the wheels. The gearbox is a part that helps change gears.
Check your transmission fluid often. Change it every 20,000 to 60,000 miles. This helps your car run well and stops big repair bills.
Manual transmissions give you more control. They are cheaper to fix. Automatic transmissions are easier to use. They help drivers feel less tired.
Listen for grinding sounds or rough gear changes. Look for leaking fluid. These signs mean there could be a problem. Fixing it early saves money.
Pick the right transmission for your needs. Take good care of it. This helps your car use less gas, feel better to drive, and last longer.
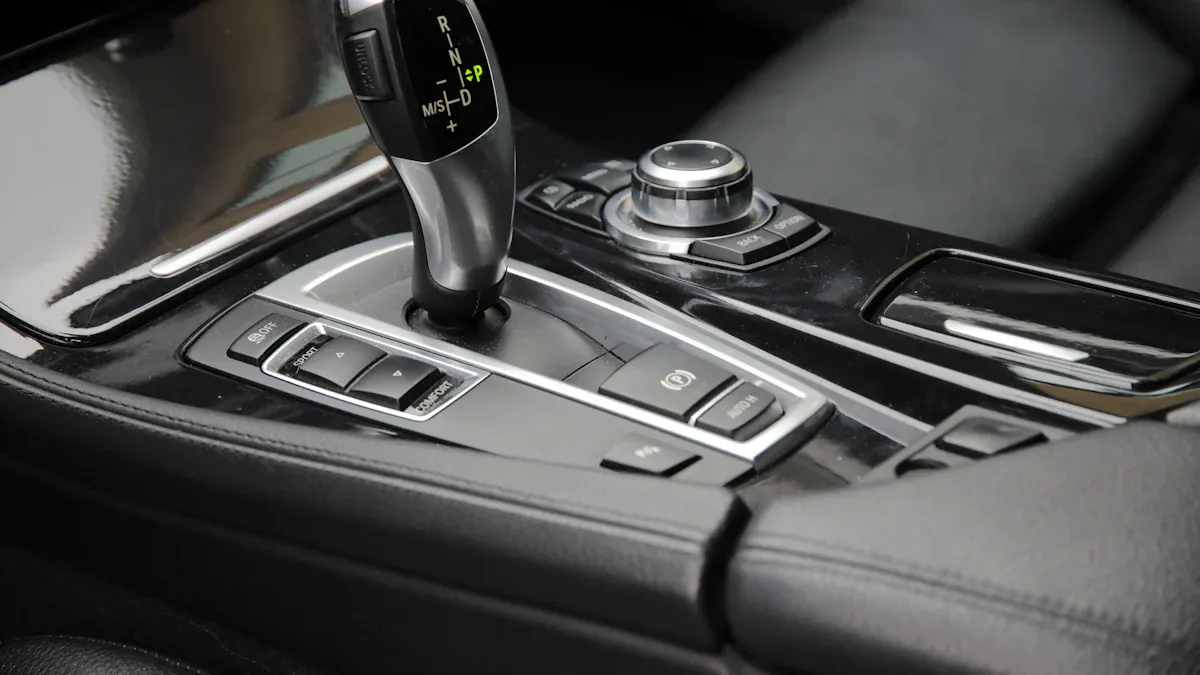

You use the transmission every time you drive your car. The transmission moves power from the engine to the wheels. It helps your car go forward, backward, and change speed. The transmission lets you drive at different speeds. This keeps the engine from working too hard. The system has many parts that work together. These parts help your car run smoothly.
Here are the main parts of a transmission in most cars:
Clutch: Connects or disconnects the engine from the transmission.
Gearbox: Changes gear ratios to adjust torque and speed.
Driveshaft: Sends power from the gearbox to the differential.
Universal joints: Let the driveshaft move as the car moves.
Differential: Splits power between the wheels so they turn at different speeds.
Drive axle: Moves power from the differential to the wheels.
Torque converter (in automatics): Connects the engine to the transmission with fluid.
Planetary gearsets: Give different gear ratios for different driving needs.
Electronic control units (ECUs): Use sensors to help with gear shifting.
Belt-and-pulley system (in CVTs): Allows for smooth, endless gear changes.
Sensors: Measure speed, throttle, and load to help the system work better.
The transmission controls how power and gears change. It keeps the engine running at the best speed for each situation. There are different types of transmissions. These include manual, automatic, and continuously variable transmissions (CVT). Each type uses its own way to change gears and control power.
The gearbox is an important part of the transmission system. The gearbox is the part that actually changes the gears. It has gears and shafts inside a strong box. When you shift gears, the gearbox changes the ratio between engine speed and wheel speed. This helps your car speed up, slow down, or climb hills. The engine does not have to work too hard.
The gearbox works by using gear trains. These are groups of gears that fit together. The gear ratio is the number of teeth on each gear. This decides how much the speed and torque change. A lower gear gives you more torque for hills. A higher gear gives you more speed for highways. The gearbox only changes speed and torque. It does not control all the power from the engine to the wheels.
Tip: If you hear grinding noises or have trouble shifting, your gearbox may need help. Regular checks and careful use can help you avoid big repair bills.
You might wonder about the difference between the transmission and the gearbox. The main difference is that the transmission is the whole system. It moves power from the engine to the wheels. The gearbox is just one part of this system. The gearbox changes the gear ratios. The transmission manages everything, like shifting, power flow, and direction.
Here is a table to help you see the differences:
Aspect | Transmission | Gearbox |
|---|---|---|
Definition | The whole system that sends power from the engine to the wheels, including clutch and other parts. | A part inside the transmission with gears to adjust torque and speed. |
Function | Controls all power flow and gear shifting. | Changes gear ratios to control speed and torque. |
Components | Gearbox, clutch, driveshaft, differential, and more. | Gears, shafts, and bearings inside a box. |
Types | Manual, automatic, semi-automatic, continuously variable. | Manual, automatic, planetary, and more. |
Maintenance Focus | Taking care of many parts. | Focus on gear condition and oil. |
You use the transmission gearbox every time you drive. You may not notice what each part does. The gearbox and transmission work together, but they are not the same. The gearbox is a part of the transmission system. The transmission gearbox changes speed and torque. The transmission manages the whole job of moving power from the engine to the wheels.
When you talk to a mechanic, knowing the difference helps you explain problems better. If you say "transmission" when you mean "gearbox," you might get the wrong repair or advice. Knowing the basics about the transmission gearbox can save you time and money.
When you start your car, the transmission starts working. It moves power from the engine to the wheels. The gearbox gets power from the engine. In manual cars, the clutch sends the power. In automatics, the torque converter does this job. Here is how the power moves:
The engine gives power to the gearbox.
The gearbox changes the gear ratio for speed or torque.
Power goes from the gearbox to the driveshaft.
The driveshaft sends power to the differential.
The differential splits power between the wheels.
The transmission control unit helps the gearbox work with other parts. This teamwork makes your car run well. It also makes driving easier for you.
Note: If you hear odd noises or feel rough shifting, the problem might be in the gearbox or another transmission part.
You change gears every time you drive your car. In a manual transmission, you press the clutch pedal. This disconnects the engine from the gearbox. You move the gear shift lever to pick a new gear. Inside the gearbox, parts slide to select the gear. Synchronizers help match gear speeds. This stops grinding sounds. Some drivers use double-clutching for smoother shifts.
Automatic transmissions use a torque converter and planetary gear sets. The transmission shifts gears for you. It opens and closes clutches inside the gearbox. Hydraulic fluid and electronic controls help pick the right gear. Dual-clutch transmissions use two clutches. This makes gear changes faster and smoother.
Smooth gear shifting keeps your engine at the best RPM. This saves fuel and helps your car last longer. More gears in new transmissions let the engine work less. This improves fuel use and lowers emissions.
You use the transmission and gearbox every time you drive. Automatic transmissions make driving easy. They shift gears for you. You do not need to think about the clutch or gear lever. This makes driving less tiring, even in traffic or on hills. Manual transmissions give you more control. But you must use the clutch and shift gears yourself. This can make you tired in stop-and-go traffic.
Aspect | Automatic Transmission | Manual Transmission |
|---|---|---|
Ease of Use | Shifts gears for you, less work needed | You shift gears and use the clutch, more skill needed |
Driver Fatigue | Less tired, good for city driving | More tired, can be hard in traffic |
Control | Transmission picks gear changes | You pick gear changes |
Comfort | More comfort, less strain | Can be less comfy with lots of clutch use |
Maintenance & Cost | More complex, costs more to fix | Simpler, cheaper to fix but needs careful use |
Most drivers want a transmission that works well and needs little care. If you keep your transmission and gearbox in good shape, you get smoother rides and fewer problems. Common problems are clutch wear, low transmission fluid, and worn synchronizers. Regular checks help you avoid these problems and keep your car running well.
You use your hands and feet to control a manual transmission gearbox. You press the clutch pedal to stop the engine from turning the gearbox. Then you move the gear stick to pick the right gear. This type lets you control when to change gears. Many people like how much control they have over the car. Manual transmission gearboxes have a flywheel, clutch, and simple gears. These gearboxes can last a long time if you drive with care. You might need to get a new clutch after many miles, but the gearbox usually does not break. Manual transmission gearboxes are cheaper to fix and take care of than other types. You see them in sports cars, cheaper cars, and trucks. They are still common in Europe and some other countries because they cost less and save fuel.
Tip: If you want to spend less on repairs and like driving, a manual transmission gearbox is a smart pick.
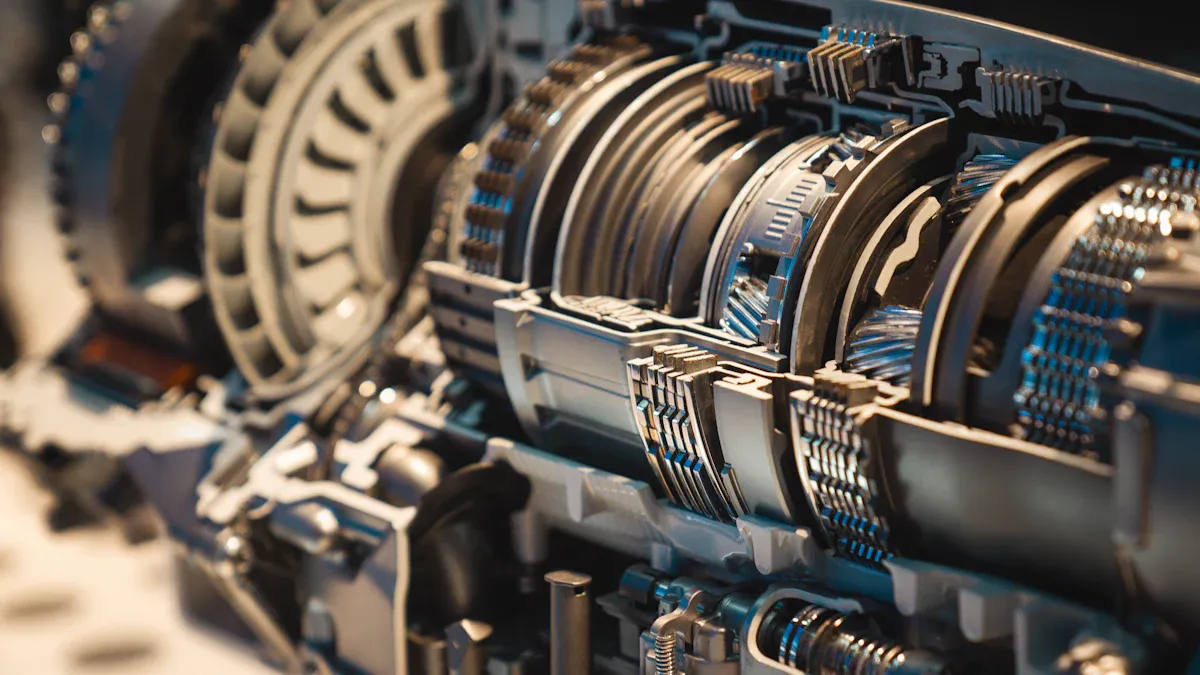
Automatic transmissions change gears for you. You do not need to press a clutch pedal or move a gear stick. These transmissions use a torque converter, planetary gearsets, and hydraulic parts to change gears smoothly. The gearbox in an automatic transmission is harder to understand than a manual one. It has clutches, bands, and sensors that work together. Most new cars have automatic transmissions because they make driving simple, even in traffic. In the United States, almost all new cars use automatic transmissions. These gearboxes need fluid changes and good care. Fixing them can cost more because the gearbox has many parts inside.
Core Component | Description & Function |
|---|---|
Planetary Gearset | Gives many gear ratios by locking and unlocking different parts. |
Torque Converter | Transfers engine power without a clutch pedal. |
Clutches & Bands | Change gears by engaging and disengaging parts inside the gearbox. |
Hydraulic System | Uses fluid to control gear changes. |
There are other types of transmission gearboxes in new cars. Some examples are:
Continuously Variable Transmission (CVT): Uses belts and pulleys for smooth gear changes. You get better gas mileage and a quiet ride.
Dual-Clutch Transmission (DCT): Has two clutches for quick, sporty gear shifts. Many fast cars use this gearbox.
Automated Manual Transmission (AMT): Looks like a manual but uses computers to shift gears for you.
Semi-Automatic Transmission: Lets you pick gears with a stick or paddle, but the clutch works by itself.
Each transmission gearbox type has its own good points. CVTs are great for city driving and saving gas. DCTs give you fast shifts and sporty driving. AMTs and semi-automatics mix control and comfort. You should pick the transmission gearbox that matches how you like to drive and what you need.
You need to keep your transmission and gearbox in good shape to avoid big repair bills. Regular care helps both systems last longer and work better. Here are the most common maintenance tasks you should follow:
Change the transmission fluid every 30,000 to 60,000 miles, or as your car’s manual says.
Replace the transmission filter when you change the fluid.
Check fluid levels often, especially if your car has a dipstick.
Look for leaks under your car and fix them right away.
Inspect the gearbox and transmission for damage or worn parts.
Avoid overloading your car to reduce strain on the transmission gearbox.
Drive smoothly to protect all transmission gearbox parts.
Maintenance costs can vary. Routine transmission care usually costs $100 to $300. If you need a new transmission, it can cost $1,800 to $8,000. Manual transmission repairs are often cheaper than automatic ones, but you may need to replace the clutch more often.
You should watch for warning signs that your transmission or gearbox needs help. Early action can save you money and keep you safe. Common problems include:
Slipping gears or rough shifting.
Grinding noises or shaking during gear changes.
Fluid leaks under your car.
Burning smells from overheating transmission fluid.
Dashboard warning lights for the transmission gearbox.
If you notice any of these, get your car checked by a professional. Problems like worn-out gears, faulty solenoids, or low fluid can cause serious damage if ignored. Regular checks help you spot issues before they get worse.
Your choice of transmission gearbox affects how much fuel your car uses. Manual transmissions can give you better control and sometimes better fuel economy. Automatic transmissions with more gears help the engine run at the best speed, saving gas. CVT transmission gearboxes use a belt system for smooth, efficient driving and can improve fuel economy by about 6%. Keeping your transmission and gearbox well-maintained also helps your car use less fuel. Smooth shifting and clean fluid reduce friction and power loss.
Tip: Watch for changes in how your car shifts or sounds. Quick action keeps your transmission gearbox running smoothly and saves you money at the pump.
You now know that a transmission is the whole system that moves power from the engine to the wheels, while a gearbox is just one part of that system. When you understand these terms, you can take better care of your car. You spot problems early and talk clearly with your mechanic. Use this knowledge to keep your transmission working well and avoid costly repairs.
A transmission gearbox is a part of your car’s transmission system. You use it to change gears. This lets you control speed and torque. Transmission gearboxes help your engine work better and last longer.
You might hear grinding noises or feel rough shifting. Sometimes, you see fluid leaks under your car. If you notice these signs, your transmission gearbox or its parts may need attention. Get your car checked soon.
You find several transmission gearbox types in cars. Manual transmission gearboxes let you shift gears yourself. Automatic transmission gearboxes shift for you. Other types include CVT and dual-clutch transmission gearboxes. Each type has different parts and benefits.
You should check your transmission gearbox fluid every 20,000 to 30,000 miles. Replace the fluid and filter as your car’s manual suggests. Regular service keeps transmission gearbox parts working well and helps avoid costly repairs.
You should not drive with a faulty transmission gearbox. Problems can get worse fast. You risk damaging other transmission gearbox parts. Always fix issues early to keep your car safe and reliable.